If you have an aging parent, it’s important to understand the difference between normal aging and signs that indicate they may need extra help at home. Recognizing these signs early allows you to make confident, informed decisions about their care, keeping them safe, comfortable, and independent.
In this guide, we’ll cover how to know when it may be time for in-home care, including seven common signs your parent may need support, typical vs. concerning changes, life events that often signal a need for care, types of in-home care services, and tips for discussing care with your loved one without conflict.
How Do You Know When It’s Time for In-Home Care?
Knowing when your parent needs home care is rarely a single moment; it’s usually a gradual realization. Many families wait until a crisis occurs, such as a fall, hospitalization, or sudden health decline. The most successful care decisions, however, happen earlier, when support can improve safety, comfort, and quality of life, instead of reacting to an emergency.
Ask yourself: Are your parents managing daily life safely? Are they keeping up with personal care, meals, medications, and household tasks? Do they seem physically stable, emotionally well, and socially engaged?
If you find yourself stepping in more frequently, or caregiving responsibilities feel overwhelming, professional in-home care can provide consistent support while allowing you to return to your role as a son or daughter, not just a caregiver.
Tip: Home care isn’t about taking away independence, it’s about protecting it. Acting proactively helps your parents remain safe at home while maintaining dignity and routine.
7 Signs Your Aging Parent May Need In-Home Care

There are several signs that an aging parent may benefit from in-home care. Recognizing these signs early helps your loved one stay safe, healthy, and supported. Watch for:
1. Difficulty with Daily Activities
If your loved one is struggling with bathing, dressing, preparing meals, or taking medications correctly may indicate a need for assistance.
Read: How Often Should Seniors Bathe? A Guide for Senior Hygiene and Safety
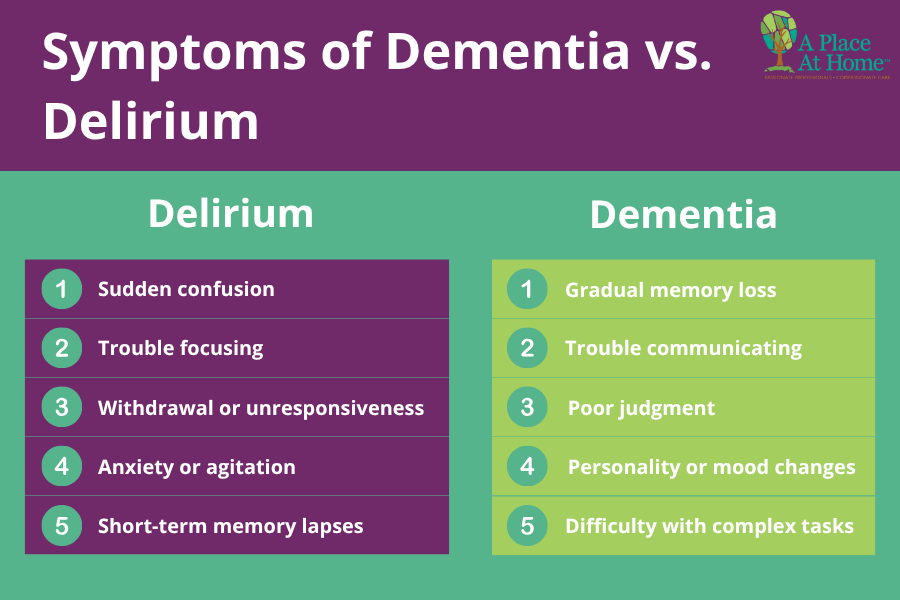
2. Memory lapses That Affect Safety
Occasional forgetfulness is normal, but frequent memory issues, such as leaving the stove on, misplacing important items, or forgetting essential routines, can put your parent at risk and may indicate the need for in-home support. According to the National Institute on Aging (NIH), Alzheimer’s disease is the most commonly diagnosed form of dementia in older adults.
3. Frequent Falls or Balance Problems
Unsteady walking, balance issues, or repeated falls require professional supervision and mobility assistance. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), falls are the leading cause of injury for adults aged 65 years and older.
4. Missed Appointments or Unpaid Bills
If your parent is regularly forgetting medical appointments, medications, or financial responsibilities, it may be time to consider help with organization, reminders, and daily management.
5. Poor Nutrition or Hygiene
Noticeable weight loss, spoiled food in the refrigerator, or a decline in personal grooming and cleanliness can indicate that your loved one is having trouble caring for themselves independently.
6. Isolation, Depression, or Anxiety
Social withdrawal, mood changes, or increased anxiety may stem from health challenges, memory loss, or limited mobility. In-home care can provide companionship, emotional support, and daily engagement.
7. Family Caregiver Burnout
If you or another family member has been providing ongoing care and feels overwhelmed, exhausted, or stretched too thin, it may be time to bring in professional help. In-home care can relieve stress while ensuring your loved one receives consistent, high-quality support.
Normal Aging vs. Warning Signs That Indicate Help Is Needed
It’s important to understand the difference between normal aging and warning signs that your loved one may need in-home care. While some changes are a natural part of getting older, others can signal that additional support is needed to maintain safety and well-being. Here are a few ways to tell the difference:
- Occasional forgetfulness without safety risks: Minor memory lapses while still managing daily life safely.
- Declining self-care, falls, or missed responsibilities: Struggling with hygiene, frequent falls, or financial tasks signals the need for support.
- Ongoing resistance despite concerns: If multiple discussions fail, involve trusted family members or healthcare professionals to help your parent understand that accepting help preserves independence.
Life Events That Often Signal a Need for In-Home Care
There are many situations in which a senior loved one may benefit from home care. While every family’s circumstances are different, the following scenarios often signal that it may be time to consider professional in-home support:
- After a hospital stay: If your loved one has recently been hospitalized, lives alone, or must follow specific medical instructions during recovery, in-home care can provide help with daily activities, medication reminders, and overall safety.
- Following a fall or emergency room visit: A fall or ER visit often leads to new challenges, such as physical therapy appointments, medication changes, or temporary mobility limitations. Professional caregivers can assist with recovery and help prevent further injury.
- After the loss of a spouse: When a spouse passes away, many seniors struggle with daily routines, loneliness, or emotional distress. In-home care can offer companionship, emotional support, and assistance with everyday tasks during this difficult transition.
- When driving becomes unsafe: If your loved one can no longer drive safely, their independence and access to essential activities may be affected. A caregiver can provide transportation to appointments, errands, and social outings, helping them remain connected and active.
- Frequent calls for help: If your parent is calling frequently because they need help with small but important tasks, it may be a sign that managing daily life alone is becoming difficult. In-home care can provide consistent support and peace of mind for both of you.
What Types of In-Home Care Are Available for Seniors?

The type of care your senior loved one needs varies based on independence, health, and lifestyle. Choosing a flexible agency ensures support evolves as needs change. Below are the common levels of in-home care, based on the amount of support required:
- A few hours a week: Some seniors need only light assistance, such as help with household tasks, errands, or occasional personal care. A caregiver can provide support for a few hours each week to maintain safety and independence.
- Daily support: For seniors who need help with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, meal preparation, or medication reminders, a caregiver may visit each day to provide consistent assistance.
- Overnight care: Overnight care ensures your loved one is safe and comfortable throughout the night. This level of care is often helpful for individuals with medical needs, sleep disturbances, or a higher risk of falls.
- 24-hour care: With 24-hour care, a team of caregivers works in rotating shifts (typically 12 hours each) so that someone is always awake and available. This provides continuous support with personal care, medications, mobility, safety, and companionship.
- Live-in care: Live-in care involves a caregiver residing in the home and providing around-the-clock assistance. This option offers ongoing supervision, personalized care, and peace of mind for families who want full-time support in a familiar environment.
It’s also important to remember that care needs often evolve. Your loved one may begin with just a few hours of help each week, but over time, may require daily, overnight, or even live-in care. That’s why choosing a home care agency that can adjust the care plan as needs change is essential for long-term support and continuity of care.
Does In-Home Care Take Away a Parent’s Independence?
It’s common for seniors to worry that care means losing independence. When discussing in-home care with your senior loved one, it’s important to approach the conversation with patience, honesty, and respect. Taking time to explain what home care truly involves can help ease concerns and reduce resistance. If your parent initially objects, here are a few ways to gently reframe the conversation:
- Emphasize support, not loss of independence: In-home care is designed to help, not take control. A caregiver helps with daily activities that may have become challenging, allowing your loved one to remain independent, safe, and comfortable in their own home.
- Highlight the benefits of aging in place: Remaining at home means your parents don’t have to adjust to a new environment, routine, or community. They can continue living in the familiar space they love, surrounded by their belongings, neighbors, and memories.
- Set clear expectations and offer reassurance: Explain what a typical day with a caregiver will look like and how the care will fit into their routine. Reassure them that you and other family members will continue to visit, support, and stay actively involved in their lives.
How to Talk to Your Parent About In-Home Care
When you begin discussing in-home care with your parents, it’s essential to approach the conversation with empathy, patience, and respect.
- Make it a shared decision: Avoid giving orders or presenting care as something that is being “done to” them. Instead, involve your parents in the decision-making process and emphasize that the goal is to choose what is best for their comfort, safety, and independence.
- Lead with concern for their well-being: Focus on your care for their safety and quality of life. Use “I” statements such as “I worry about you being alone after your fall” and choose a calm, private time and place where they feel comfortable. Be understanding and clearly explain the benefits of the care option you’re discussing.
- Seek support if the conversation stalls: If your parent is resistant to the idea of in-home care, consider involving trusted family members, close friends, or even a healthcare professional. Hearing consistent, compassionate messages from others can help reinforce that accepting help is about staying safe and independent, not giving up control.

Feeling Confident About Choosing In-Home Care
Choosing in-home care for a loved one is a meaningful decision, and it’s natural to want reassurance that you’ve made the right choice. The following signs can help you feel confident in your decision:
- You feel supported by the care agency: If your home care company communicates clearly, treats you with respect, and consistently meets your loved one’s needs through proper caregiver training, appropriate scheduling, and a strong caregiver-client match, it’s a strong indication that you’ve chosen well.
- The care plan adapts as needs change: A quality in-home care provider will be flexible and responsive, adjusting hours, services, and caregiver support as your loved one’s condition evolves.
- You know it’s okay to ask for guidance: You don’t have to navigate this journey alone. Home care professionals, support groups, and experienced caregivers can offer valuable insight, reassurance, and perspectives you may not have considered. Reaching out for help is not a sign of uncertainty; it’s a sign of thoughtful, proactive care.
Professional Senior Home Care from A Place At Home – Newton
Recognizing when your parents may need in-home care is not about giving up control; it’s about protecting their safety, dignity, and quality of life. When the right support is in place, your loved ones can continue living comfortably at home while you gain peace of mind knowing they’re receiving dependable, compassionate care.
At A Place At Home – Newton, we provide personalized senior home care, from a few hours per week to live-in care. Our trained caregivers ensure safety, independence, and companionship for every stage of your parent’s life.
If you’re noticing signs that your parents may need help or simply want guidance on your next steps, we’re here for you. Contact A Place At Home – Newton at (857) 999-0301 today to schedule a free, no-obligation in-home consultation. Together, we’ll create a care plan that brings comfort, confidence, and peace of mind to your entire family.
Frequently Asked Questions About In-Home Care for Parents
At what age do most seniors need in-home care?
There is no specific age at which seniors require in-home care, as it depends on health, mobility, and lifestyle. Some adults may need support in their late 60s, while others remain independent well into their 80s or 90s. The key is to focus on functional abilities rather than age. If your loved one struggles with daily activities or safety, it’s time to consider care.
Is in-home care better than assisted living?
In-home care supports independence in a familiar environment, while assisted living offers structured, 24-hour support and community amenities.
How many hours of care should we start with?
The number of care hours needed varies based on your parents’ level of independence. Some seniors may only need a few hours per week for light assistance, while others benefit from daily visits or overnight support. Many families start with a smaller plan and adjust as needs change. Consulting a professional in-home care provider can help determine the right starting point.
What if my parents refuse help?
Approach conversations with empathy, involve trusted family or professionals, and emphasize that care allows them to stay safe at home.